This Excel VBA tutorial explains how to use Workbook.SaveAs Method.
You may also want to read:
Excel VBA convert CSV to Excel
Excel VBA Workbook.SaveAs Method
VBA Workbook.SaveAs Method is same as the action Save As
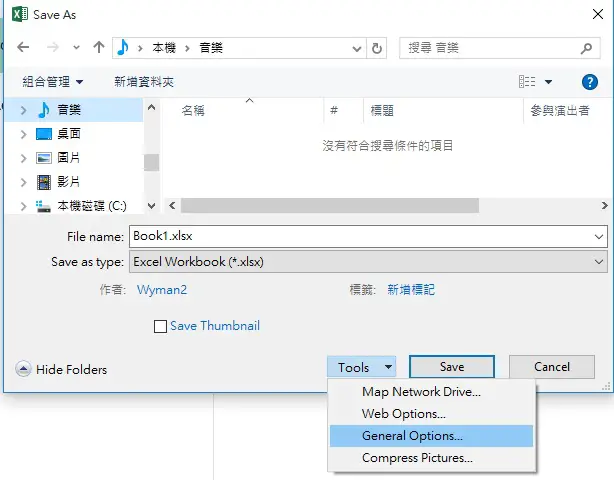
The options under Tools are also available in VBA Workbook.SaveAs Method.
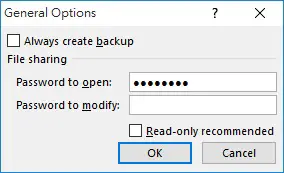
For example, we can add password to workbook.
To understand what Workbook.SaveAs Method is capable of, let’s see what arguments it has.
Syntax – Excel VBA Workbook.SaveAs Method
expression .SaveAs(FileName, FileFormat, Password, WriteResPassword, ReadOnlyRecommended, CreateBackup, AccessMode, ConflictResolution, AddToMru, TextCodepage, TextVisualLayout, Local)
| Name | Required/Optional | Data Type | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Filename | Optional | Variant | A string that indicates the name of the file to be saved. You can include a full path; if you don’t, Microsoft Excel saves the file in the current folder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FileFormat | Optional | Variant | The file format to use when you save the file. For a list of valid choices, see the XlFileFormat enumeration. For an existing file, the default format is the last file format specified; for a new file, the default is the format of the version of Excel being used.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Password | Optional | Variant | A case-sensitive string (no more than 15 characters) that indicates the protection password to be given to the file. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WriteResPassword | Optional | Variant | A string that indicates the write-reservation password for this file. If a file is saved with the password and the password isn’t supplied when the file is opened, the file is opened as read-only. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ReadOnlyRecommended | Optional | Variant | True to display a message when the file is opened, recommending that the file be opened as read-only. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CreateBackup | Optional | Variant | True to create a backup file. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AccessMode | Optional | XlSaveAsAccessMode | The access mode for the workbook.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ConflictResolution | Optional | XlSaveConflictResolution | An XlSaveConflictResolution value that determines how the method resolves a conflict while saving the workbook. If set to xlUserResolution, the conflict-resolution dialog box is displayed. If set to xlLocalSessionChanges, the local user’s changes are automatically accepted. If set to xlOtherSessionChanges, the changes from other sessions are automatically accepted instead of the local user’s changes. If this argument is omitted, the conflict-resolution dialog box is displayed.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AddToMru | Optional | Variant | True to add this workbook to the list of recently used files. The default value is False. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TextCodepage | Optional | Variant | Ignored for all languages in Microsoft Excel.
When Excel saves a workbook to one of the CSV or text formats, which are specified by using the FileFormat parameter, it uses the code page that corresponds to the language for the system locale in use on the current computer. This system setting is available in the Control Panel, by clicking Region and Language, clicking the Location tab, under Current location. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TextVisualLayout | Optional | Variant | Ignored for all languages in Microsoft Excel.
When Excel saves a workbook to one of the CSV or text formats, which are specified by using the FileFormat parameter, it saves these formats in logical layout. If left-to-right (LTR) text is embedded within right-to-left (RTL) text in the file, or vice versa, logical layout saves the contents of the file in the correct reading order for all languages in the file without regard to direction. When an application opens the file, each run of LTR or RTL characters are rendered in the correct direction according to the character value ranges within the code page. (Unless an application that is designed to display the exact memory layout of the file, such as a debugger or editor, is used to open the file.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Local | Optional | Variant | True saves files against the language of Microsoft Excel (including control panel settings). False (default) saves files against the language of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) (which is typically US English unless the VBA project where Workbooks.Open is run from is an old internationalized XL5/95 VBA project). |
Example – Excel VBA Workbook.SaveAs Method
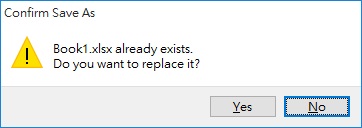
When you save as a workbook in a location where the workbook name already exists, you will receive the following prompt box.
In order for the Macro to continue to run without prompting the box, the first thing to do is to temporarily turn the alert box off using Application.DisplayAlerts = False, and all answers will become Yes.
The second thing is the Filname argument. Although the documentation says if you omit the Filename, the current folder will be used. I tried with Excel 2013 but it saves to My Document folder, so I use Application.ActiveWorkbook.FullName to make sure the file really saves to the current folder.
The third thing is FileFormat. I choose xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled (xlsm) to ensure the Macro is saved successfully.
The below procedure uses SaveAs Method to add password (yourpassword) and then overwrite the existing xlsm workbook.
Sub add_password() Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs Filename:=Application.ActiveWorkbook.FullName, FileFormat:=xlOpenXMLWorkbookMacroEnabled, Password:="yourpassword" 'OR using specific path 'ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs "C:\folderA\test.xlsx", Password:="yourpassword" Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
Outbound References
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/office/ff841185.aspx