This Excel tutorial explains how to use Excel Lookup Function and how to look up multiple criteria.
You may also want to read:
Excel Vlookup second matched value or specific occurence
Excel Lookup Function lookup multiple criteria not in the first column
Excel lookup partial text using Vlookup with Wildcard
Excel Lookup Function – lookup multiple criteria
Excel Lookup Function is to look up a value in a Range (or array) and return the corresponding result in another Range (or array). Note that “Range” is also known as “Vector” if you read other tutorial.
Differences between Lookup and Vlookup
First of all, lets recap the syntax of Vlookup
VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
Lookup Function behaves similarly as Vlookup if the last parameter [range_lookup] of vlookup is set to TRUE.
TRUE means to look for similar match, FALSE means to look for exact match. It is not helpful to look for similar match in 99% situations because it may not return the exact result we want. In Lookup Function, we cannot choose to look for exact match or similar match, we can only look for similar match.
In order to make an apple to apple comparison, I will talk about how Lookup behaves differently against Vlookup with FALSE [range_lookup] below.
1 – For Lookup Function, lookup Range must be in ascending order. Vlookup (last Function parameter =FALSE) does not have such requirement.
2 – Lookup Function can look up value not in the first column of lookup Range, because you can specify the lookup Range anywhere instead of specifying the Nth column in lookup table
3 – If there are more than one matched results, Vlookup (last Function parameter =FALSE) returns the first matched value, while Lookup returns the last matched value
3 – If Lookup Function cannot find an exact match, it returns the largest value in the lookup Range that is less than or equal to the lookup value (behave the same way as Vlookup when the last parameter is set to TRUE). While you can easily identify which is larger for numeric value (for example, 1000 > 10).
For text like alphabets or symbols, the comparison is based on ASCII value of the text (for example, a> A >?> 1), read the references at the bottom of the post for ASCII value and text conversion.
Therefore even if there is no match, Lookup Function may still return a value, while Vlookup returns #N/A.
Syntax of Lookup Function
LOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_range, result_range)
| lookup_value | A Range or array that LOOKUP searches for |
| lookup_range | A lookup Range or array that contain only one row or one column, must be sorted in ascending order |
| result_range | Optional. A range that contains only one row or column. |
Click here to see the detailed explanation.
Example of Lookup Function
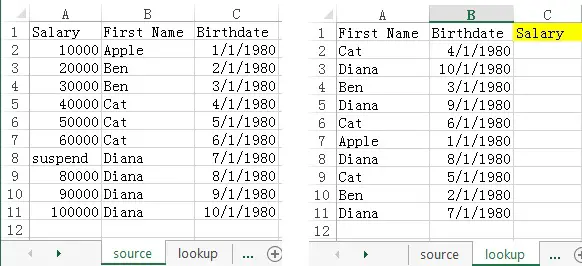
In this example, we have two worksheets:
1) source – the source table being looked up
2) lookup – the lookup table in which you want to lookup salary from source
First Name and Birthdate are keys to identify an unique person.
| Formula | Result | Explanation |
| =LOOKUP(B2,source!C2:C11,source!A2:A11) | 40000 | Look up Salary where Birthdate is 4/1/1980 |
| =LOOKUP(“Cat”,source!B2:B11,source!A2:A11) | 60000 | Look up Salary where First Name is Cat. Because there are more than 1 Cat, result of last Cat is returned. |
| =LOOKUP(“C”,source!B2:B11,source!A2:A11) | 30000 | “C” cannot be found in lookup Range, so the Function would return the largest value less than “C”, which is the last “Ben” |
| =LOOKUP(“A”,source!B2:B11,source!A2:A11) | #N/A | “A” cannot be found in lookup Range, so the Function would return the largest value less than “A”, but the smallest in the lookup Range is “Apple”, so nothing is smaller than “A” |
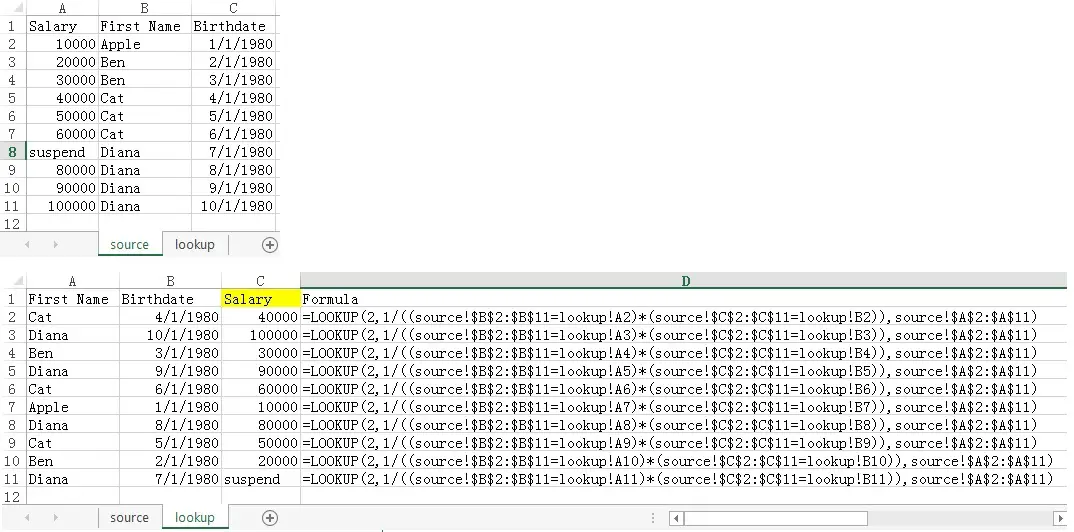
Advanced use of Lookup Function – lookup multiple criteria
Apply the lookup formula as below in column C. Column D is to show the actual formula of column C.
Let’s take a look at the formula at D2
=LOOKUP(2,1/((source!$B$2:$B$11=lookup!A2)*(source!$C$2:$C$11=lookup!B2)),{10000;20000;30000;...})
| Parameter name | Parameter value |
| lookup_value | 2 |
| lookup_range | 1/((source!$B$2:$B$11=lookup!A2)*(source!$C$2:$C$11=lookup!B2)) |
| result_range | source!$A$2:$A$11 |
Below is the mechanism of the formula.
=LOOKUP(2,1/((source!$B$2:$B$11=lookup!A2)*(source!$C$2:$C$11=lookup!B2)),source!$A$2:$A$11)
=LOOKUP(2,1/({Apple;Ben;Ben;Cat;...="Cat"}*{29221;29222;29223;29224;...=29224}),{10000;20000;30000;40000;...})
=LOOKUP(2,1/({FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;...}*{FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;...}),{10000;20000;30000;40000;...})
=LOOKUP(2,1/{0;0;0;1;...},{10000;20000;30000;40000;...})
=LOOKUP(2,{#DIV/0;#DIV/0;#DIV/0;1;...},{10000;20000;30000;40000;...})
=40000
In the second parameter
1/{0;0;0;1;…}
The reason for dividing an array by 1 is that we want to turn all “0” to non numerical value (i.e. error)
{#DIV/0;#DIV/0;#DIV/0;1;...}
Afterwards, we apply LOOKUP formula and use “2” as the lookup_value parameter, where “2” is a constant that can be applied to other formula. When we lookup a value (2) which cannot be found in the array (a combination of 1 and #DIV/0), the Function will match the largest value (1) in the lookup_range (1 and #DIV/0) that is less than or equal to the value (2). In fact, you can also use “1” as the lookup_value parameter assume that value 1 can be found in the array, the Function will return the last matched value as well. As a normal practice, people tend to use “2” as parameter.
References – ASCII value of text
Note the conversion of Dec and Char
| Dec | Hex | Oct | Char | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 000 | null | |
| 1 | 1 | 001 | start of heading | |
| 2 | 2 | 002 | start of text | |
| 3 | 3 | 003 | end of text | |
| 4 | 4 | 004 | end of transmission | |
| 5 | 5 | 005 | enquiry | |
| 6 | 6 | 006 | acknowledge | |
| 7 | 7 | 007 | bell | |
| 8 | 8 | 010 | backspace | |
| 9 | 9 | 011 | horizontal tab | |
| 10 | A | 012 | new line | |
| 11 | B | 013 | vertical tab | |
| 12 | C | 014 | new page | |
| 13 | D | 015 | carriage return | |
| 14 | E | 016 | shift out | |
| 15 | F | 017 | shift in | |
| 16 | 10 | 020 | data link escape | |
| 17 | 11 | 021 | device control 1 | |
| 18 | 12 | 022 | device control 2 | |
| 19 | 13 | 023 | device control 3 | |
| 20 | 14 | 024 | device control 4 | |
| 21 | 15 | 025 | negative acknowledge | |
| 22 | 16 | 026 | synchronous idle | |
| 23 | 17 | 027 | end of trans. block | |
| 24 | 18 | 030 | cancel | |
| 25 | 19 | 031 | end of medium | |
| 26 | 1A | 032 | substitute | |
| 27 | 1B | 033 | escape | |
| 28 | 1C | 034 | file separator | |
| 29 | 1D | 035 | group separator | |
| 30 | 1E | 036 | record separator | |
| 31 | 1F | 037 | unit separator | |
| 32 | 20 | 040 | space | |
| 33 | 21 | 041 | ! | |
| 34 | 22 | 042 | “ | |
| 35 | 23 | 043 | # | |
| 36 | 24 | 044 | $ | |
| 37 | 25 | 045 | % | |
| 38 | 26 | 046 | & | |
| 39 | 27 | 047 | ‘ | |
| 40 | 28 | 050 | ( | |
| 41 | 29 | 051 | ) | |
| 42 | 2A | 052 | * | |
| 43 | 2B | 053 | + | |
| 44 | 2C | 054 | , | |
| 45 | 2D | 055 | – | |
| 46 | 2E | 056 | . | |
| 47 | 2F | 057 | / | |
| 48 | 30 | 060 | 0 | |
| 49 | 31 | 061 | 1 | |
| 50 | 32 | 062 | 2 | |
| 51 | 33 | 063 | 3 | |
| 52 | 34 | 064 | 4 | |
| 53 | 35 | 065 | 5 | |
| 54 | 36 | 066 | 6 | |
| 55 | 37 | 067 | 7 | |
| 56 | 38 | 070 | 8 | |
| 57 | 39 | 071 | 9 | |
| 58 | 3A | 072 | : | |
| 59 | 3B | 073 | ; | |
| 60 | 3C | 074 | < | |
| 61 | 3D | 075 | = | |
| 62 | 3E | 076 | > | |
| 63 | 3F | 077 | ? | |
| 64 | 40 | 100 | @ | |
| 65 | 41 | 101 | A | |
| 66 | 42 | 102 | B | |
| 67 | 43 | 103 | C | |
| 68 | 44 | 104 | D | |
| 69 | 45 | 105 | E | |
| 70 | 46 | 106 | F | |
| 71 | 47 | 107 | G | |
| 72 | 48 | 110 | H | |
| 73 | 49 | 111 | I | |
| 74 | 4A | 112 | J | |
| 75 | 4B | 113 | K | |
| 76 | 4C | 114 | L | |
| 77 | 4D | 115 | M | |
| 78 | 4E | 116 | N | |
| 79 | 4F | 117 | O | |
| 80 | 50 | 120 | P | |
| 81 | 51 | 121 | Q | |
| 82 | 52 | 122 | R | |
| 83 | 53 | 123 | S | |
| 84 | 54 | 124 | T | |
| 85 | 55 | 125 | U | |
| 86 | 56 | 126 | V | |
| 87 | 57 | 127 | W | |
| 88 | 58 | 130 | X | |
| 89 | 59 | 131 | Y | |
| 90 | 5A | 132 | Z | |
| 91 | 5B | 133 | [ | |
| 92 | 5C | 134 | \ | |
| 93 | 5D | 135 | ] | |
| 94 | 5E | 136 | ^ | |
| 95 | 5F | 137 | _ | |
| 96 | 60 | 140 | ` | |
| 97 | 61 | 141 | a | |
| 98 | 62 | 142 | b | |
| 99 | 63 | 143 | c | |
| 100 | 64 | 144 | d | |
| 101 | 65 | 145 | e | |
| 102 | 66 | 146 | f | |
| 103 | 67 | 147 | g | |
| 104 | 68 | 150 | h | |
| 105 | 69 | 151 | i | |
| 106 | 6A | 152 | j | |
| 107 | 6B | 153 | k | |
| 108 | 6C | 154 | l | |
| 109 | 6D | 155 | m | |
| 110 | 6E | 156 | n | |
| 111 | 6F | 157 | o | |
| 112 | 70 | 160 | p | |
| 113 | 71 | 161 | q | |
| 114 | 72 | 162 | r | |
| 115 | 73 | 163 | s | |
| 116 | 74 | 164 | t | |
| 117 | 75 | 165 | u | |
| 118 | 76 | 166 | v | |
| 119 | 77 | 167 | w | |
| 120 | 78 | 170 | x | |
| 121 | 79 | 171 | y | |
| 122 | 7A | 172 | z | |
| 123 | 7B | 173 | { | |
| 124 | 7C | 174 | | | |
| 125 | 7D | 175 | } | |
| 126 | 7E | 176 | ~ | |
| 127 | 7F | 177 | DEL |