This SPSS Excel tutorial explains how to run Simple Linear Regression in SPSS and Excel.
You may also want to read:
SPSS Excel Multiple Regression
Simple Linear Regression
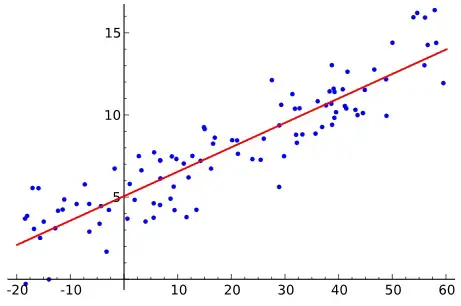
Regression analysis is to predict the value of one interval variable based on another interval variable(s) by a linear equation. We draw a random sample from the population and draw the best fitting straight line in order to estimate the population. The straight line is known as least squares or regression line.
If the linear regression model only has one independent variable, we call it simple linear regression. For multiple independent variables, we call it multiple linear regression.
The regression line equation of simple linear regression is represented as
Y = a + bX (same as y=mx + c which we learned in elementary school) where X is the independent variable Y is the dependent variable b is the slope of the line a is the intercept
In order to find the equation, we use Least Squares Method to help us find a (intercept) and b (slope).
Simple Linear Regression – semi-auto calculation
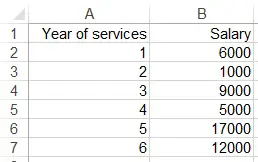
Assume that we want to analyze the relationship between year of services and salary, we draw a sample of 6 employees as below.
In this example, Year of services is an independent variable (X), while Salary is a dependent variable (Y).
First of all, calculate the sample covariance x y using COVARIANCE.S Function
=COVARIANCE.S(A2:A7, B2:B7) =7400
Next, calculate sample variance of X using VAR.S Function
=VAR.S(A1:A7) =3.5
To calculate the slope, use formula
slope b = covariance x y / variance of x = 7400/3.5 = 2114.286
Alternatively, we can calculate slope using Slope Function
=SLOPE(array y, array x) =SLOPE(B2:B7,A2:A7) =2114.286
To calculate the y-intercept, use formula
mean of y = slope * (mean of x) + y-intercept
y-intercept = mean of y - slope * (mean of x)
= 8333.333333 -2114.286 * 3.5
= 933.3333
Alternatively, we can calculate intercept using INTERCEPT Function
=INTERCEPT(array y, array x)
=933.3333
Thus, least square line is
Y = 933.3333 + 2114.286X
Simple Linear Regression – using Excel Data Analysis
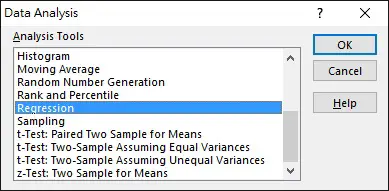
Before we begin, make sure you have installed Analysis Toolpak Add-in
Navigate to DATA tab > Data Analysis > Regression > OK
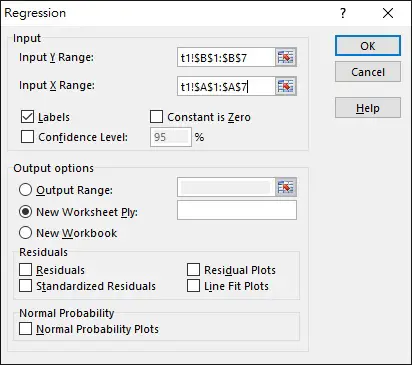
Select the data Range as below. Note that X Range is the independent variable while Y Range is the dependent variable.
Click on OK.
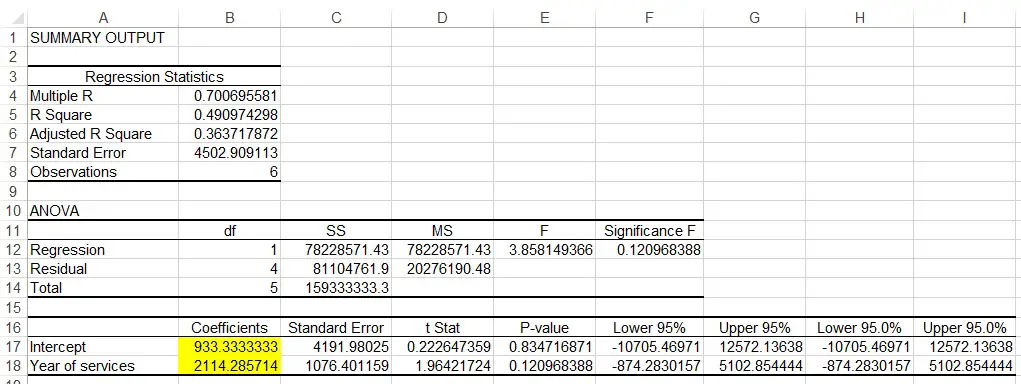
Regression Statistics Table
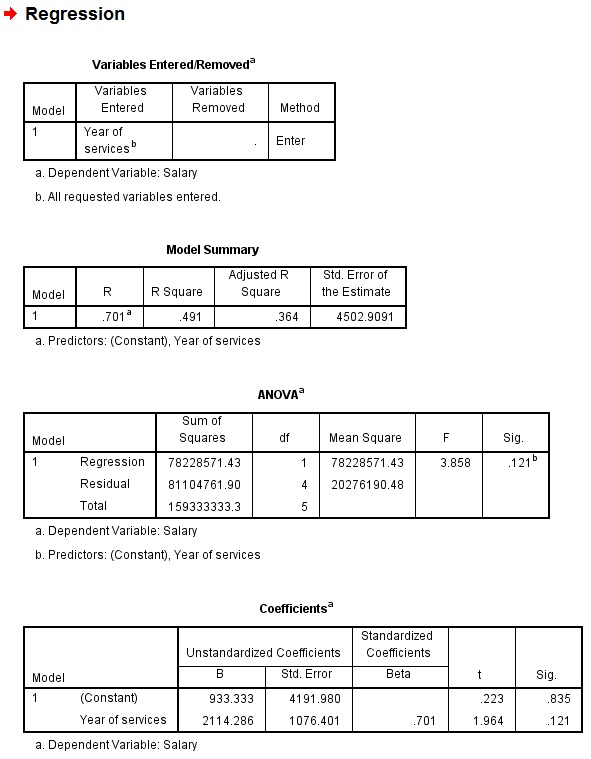
Multiple R is known as Multiple Coefficient of Correlation. +1 is a linear relation, 0 is no relation, -1 is negative linear relation. In our example, 0.7 shows a strong positive relation.
R Square is known as Coefficient of Determination, it measures how many percentage of variation in Y can be explained by variation in X, it is 49% in our example.
ANOVA Table
This table is to test the significance of the Regression model, which is >0.05 in our example (not significant)
The last table
Coefficients of Intercept means the Intercept, while Coefficients of Year of services mean the slope. Thus the least square line is
Y = 933.3333 + 2114.286X
Another important value is P-value, it shows that how significant of each factor is in the Regression model. In our example, P value of year of services is 0.12, which is larger than 0.05, meaning Year of Services is not a strong predictor in salary.
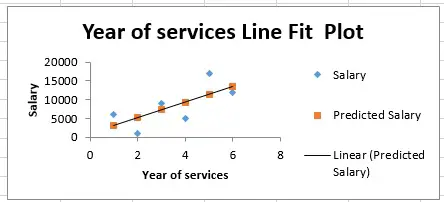
Visualization of regression line
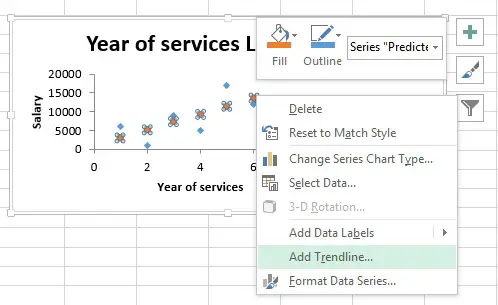
Before we generate the result, there is a check box called Line Fit Plots. If we check the box, we can visually see the least square line.
Right click on the Predicted Salary orange dots > Add Treadline
Now we have the least square line instead of dots.
According to the graph, when year of services = 2, salary should be 5000 something.
Substitute x = 2 in the regression line formula Y = 933.3333 + 2114.286X
We got Y = 5161.905
Simple Linear Regression – using SPSS
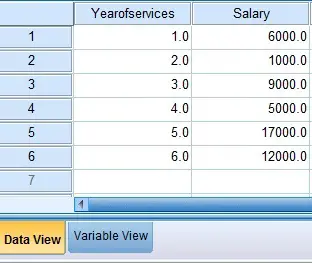
Prepare the data source as below
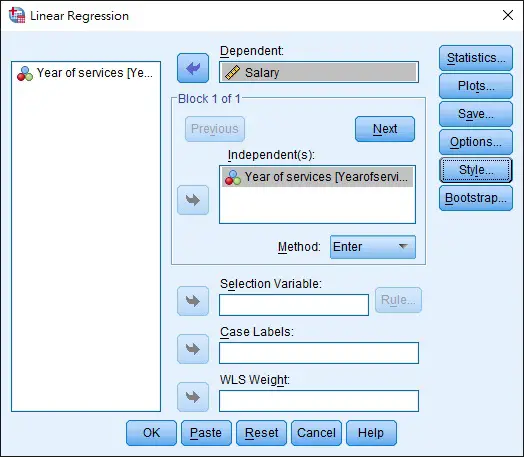
Navigate to Analyze > Regression > Linear
Select Dependent variable and Independent variable as below > OK
The table results and the structures are basically the same as the Excel output.